Bitcoin (BTC) seems to be on everyone’s mind lately as the world recently witnessed the price of BTC take a rather unexpected bearish turn this month. On January 21, 2022, Bitcoin reached six-month lows, sinking below $40,000 for the first time in months.
While some panicked, other industry experts pointed out that the Bitcoin network has become verifiably stronger than ever before. The growth of the Bitcoin network has become apparent, as hash rate figures for BTC continue to set new highs this month. For example, on Jan. 22, the BTC network recorded an all-time high of 26.643 trillion with an average hash rate of 190.71 exahash per second (EH/s).
The hash rate will continue to grow, which is a good thing
Samir Tabar, chief strategy officer at Bit Digital — a publicly listed Bitcoin miner — told Cointelegraph that the BTC hash rate refers to the amount of computing power being contributed to the network at any given time. Tabar explained that when it comes to Bitcoin mining, a higher hash rate equates to a good hash rate. “The more computing power going towards maintaining a network, the more secure it will be and the more transactions it will be able to handle,” said Tabar.
As such, the recent hash rate figures for Bitcoin are extremely notable, even with the price of BTC being down. Peter Wall, CEO of crypto mining firm Argo Blockchain, told Cointelegraph that he wasn’t surprised to see the BTC hash rate hit close to 200 EH/s. Wall further stated that even with events that have recently disrupted BTC mining hash rate like the political upheaval in Kazakhstan, the hash rate will continue to grow higher each month:
“Argo Blockchain’s mining margin last year in 2021, which is our revenue minus our direct costs, was over 80%. It was a very good year for miners. In 2020, where BTC prices were much lower, our margin was 41%. So, this year I think we will still see strong margins in the space despite the recent drop in the price of Bitcoin and the increase in the hash rate.”
Darin Feinstein, co-founder and co-chairman of Core Scientific — a major publicly-traded blockchain infrastructure provider — told Cointelegraph that based on previous Bitcoin mining hash rate data, the BTC network grew by 200% following the mass exodus of miners from China:
“The Bitcoin network one year ago was approximately 143 EH/s. Following the mining ban in China, the network fell to 63 EH/s. Today, the hash rate has grown to approximately 198 EH/s. This recent increase represents three important metrics. One, it represents a 130 EH hash rate increase on the network. Two, it represents 130 EH of new hosting infrastructure and primarily new generation hardware deployment and three, this deployment has taken place in geographic regions that use far cleaner energy than the energy used in China.”
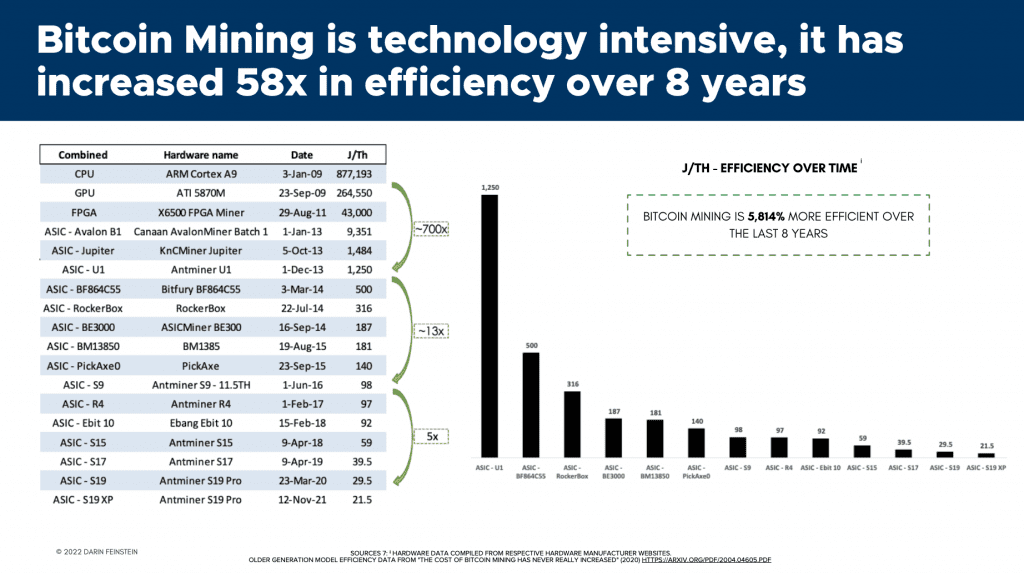
With this in mind, Feinstein noted that even though the BTC network has hit all-time highs in terms of EH/s, due to the massive improvements in miner chip technology and geographic distribution away from China, the network is now the most efficient and sustainable than it has ever been. Feinstein added that this data is important because it shows how much energy every terahash uses, which is generally represented by a metric called jules/terahash. He noted that this ratio has fallen greatly over the last several years, demonstrating a major increase in mining energy efficiency.
Will infrastructure support network growth?
Michael Levitt, co-founder chairman and CEO of Core Scientific, told Cointelegraph that he fully anticipates for the BTC global hash rate to continue growing at an aggressive pace.
However, Levitt mentioned that this growth is dependent on the price of Bitcoin moving forward, along with the success of the infrastructure currently being built. “The amount of infrastructure expected will be challenged by global supply chain issues,” he remarked.
Feinstein added that infrastructure is the biggest challenge when it comes to mining Bitcoin. “The bottlenecks for Bitcoin mining are land, energy, equipment, and lastly, infrastructure. There is plenty of ASIC hardware to be purchased, energy and land are also readily available, but miners need a place to plug in power, and, historically, that is where miners run into issues,” he commented.
North America has become one of the world’s largest Bitcoin mining hubs, as per data from the Cambridge Bitcoin Electricity Consumption Index, which shows that 35% of the average monthly BTC hash rate comes from the United States, while 10% comes from Canada. Wall explained that North America has taken the lead as a global Bitcoin mining hub for a number of reasons. “This is the case due to the region’s crypto-friendly jurisdiction, its stable regulatory environment, pro-innovation nature and, most importantly, access to the most important thing miners need — low-cost power, preferably renewable.”
Wall elaborated that the low costs of power in the U.S. have been significant for miners, especially when organizations tap into the right part of the power grid. “We’ve seen significant growth in Texas over the last 12 months,” he said.
Cointelegraph previously reported that the Bitcoin mining industry in Texas consumed around 500 to 1,000 megawatts (MW) of power during Nov. 2021. The Electric Reliability Council of Texas reportedly anticipates that demand could increase as much as fivefold by 2023 and has planned an additional 3,000 to 5,000 MW.
Wall elaborated that many miners are moving to Texas due to the fact that the state operates its own power grid that consists of a high degree of power from sustainable generation sources, but needs more flexible demand, or load:
“Miners can provide a consistent load that is flexible. It’s also helpful that Texas has demand response programs in place, where miners will shut down and give power back to the grid when there is high demand. This makes the grid more resilient.”
Benefits such as these have prompted Argo Blockchain to build its next 200 MW facility in Dickens County, west Texas, directly next to a 5.5-gigawatt substation. “There is a lot of congestion at that substation and they need local load to relieve it. The power from west Texas needs to go a long way to reach major urban cities like Dallas and Houston. But, if we can use that energy much closer to where it’s being generated, that relieves the congestion,” remarked Wall.
By drawing power from a nearby substation, Argo Blockchain is demonstrating the use of sustainable energy. According to Wall, the mining company has been carbon negative since 2020. This is important, as Tabar stated that a massive environmental, social and governance movement is currently facing the crypto mining industry:
“Miners must draw from clean sources of power or else they will be regulated out of business. It can’t always be about the cheapest sources of power. Miners will eventually suffer valuation discounts if they use dirty power, even if that source is cheap.”
The perks of going public
A rush of mining firms to go public is another trend the Bitcoin mining industry is likely to witness this year. Most recently, Texas-based Bitcoin mining company Rhodium announced plans to offer 7.69 million shares at $12–$14 each in an initial public offering (IPO).
Core Scientific went public on Jan. 20 after merging with Power & Digital Infrastructure Acquisition in aSPAC transaction. Although shares of Core Scientific have fallen since then, Feinstein mentioned that every publicly listed crypto company — like Coinbase, Galaxy Digital and others — brings institutional investment opportunities to the U.S. market. “This is enhancing and bringing credibility to the entire industry,” he remarked.
Levitt added that Bitcoin miners going public brings about a number of benefits, including better access to capital while having publicly traded equity that can be used for acquiring and building other businesses. Moreover, Levitt added that having a public presence is useful for conversations in and around the financial services industry. “However, the principal benefit is much more ready access to capital for growing and developing our business,” said Levitt.